
假设人类仍在犯错误,有时会损失数十亿美元,而人工智能是一种可能的替代方案,可以应用于导航,以减少事故数量。
2 - 模拟器为了创建一个人工智能代理来控制船只,我们需要一个环境,在这个环境中,人工智能代理可以执行导航体验,并通过自己的错误学习如何正确地导航整个通道。此外,由于我们不能使用真实的船只来训练AI代理,最好的替代方法是使用模拟真实船只动态行为的模拟器。为此,我们可以使用现有的商业软件,但在本教程中,我们将创建自己的船舶模拟器。
为此,采用了一些假设,例如:船是刚体,在船上唯一的外力是水阻力(无风,无水流),而推进力和方向舵控制力是用来控制船的方向和速度。控制船舶动力学的完整方程是复杂的。在这里,我们将使用一个非常简单的3DOF模型:
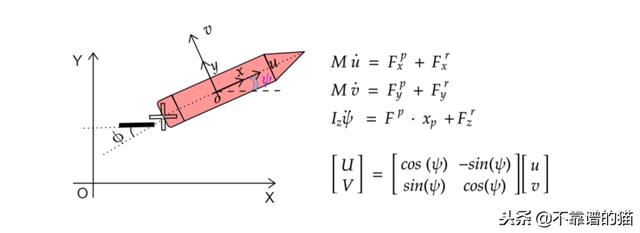
现在我们有模型微分方程,我们可以使用积分器来构建我们的模拟器。让我们写下我们的模拟器。
第1步:模拟器方程。写上面的方程式隔离加速度项我们有:
def simulate_scipy(self, t, global_states): local_states = self._global_to_local(global_states) return self._local_ds_global_ds(global_states[2], self.simulate(local_states)) def simulate(self, local_states): """ :param local_states: Space state :return df_local_states """ x1 = local_states[0] # u x2 = local_states[1] # v x3 = local_states[2] # theta (not used) x4 = local_states[3] # du x5 = local_states[4] # dv x6 = local_states[5] # dtheta Frx, Fry, Frz = self.compute_rest_forces(local_states) # Propulsion model Fpx, Fpy, Fpz = self.compute_prop_forces(local_states) # Derivative function fx1 = x4 fx2 = x5 fx3 = x6 # main model simple fx4 = (Frx Fpx) / (self.M) fx5 = (Fry Fpy) / (self.M) fx6 = (Frz Fpz) / (self.Iz) fx = np.array([fx1, fx2, fx3, fx4, fx5, fx6]) return fx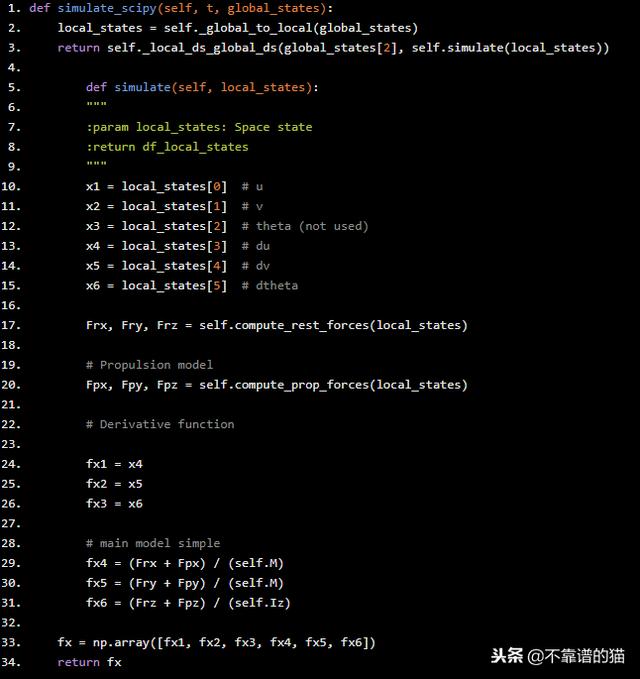
因为我们使用全局引用(OXY)来定位船舶,使用局部引用(oxyz)来积分方程,所以我们定义了一个“mask”函数来在积分器中使用。该函数将函数模拟输出的微分向量基本转换为全局引用。
def simulate_scipy(self, t, global_states): local_states = self._global_to_local(global_states) return self._local_ds_global_ds(global_states[2], self.simulate(local_states))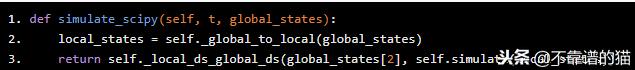
在第一行中我们存储当前动作向量,在第二行中我们使用RK45 self.integrator.step()进行积分,直到它达到最终时间跨度。最后通过 self.integrator对self.last_global_state, self.last_local_state和积分区间进行了更新。。最后,我们返回全局状态self.last_global_state。
Step4:reset函数。reset函数用于在每次新迭代(例如初始位置和速度)下设置模拟的初始条件。它使用全局变量并更新self.last_global_state,self.last_local_state。
def reset_start_pos(self, global_vector): x0, y0, theta0, vx0, vy0, theta_dot0 = global_vector[0], global_vector[1], global_vector[2], global_vector[3], global_vector[4], global_vector[5] self.last_global_state = np.array([x0, y0, theta0, vx0, vy0, theta_dot0]) self.last_local_state = self._global_to_local(self.last_global_state) self.current_action = np.zeros(2) self.integrator = self.scipy_runge_kutta(self.simulate_scipy, self.get_state(), t_bound=self.time_span)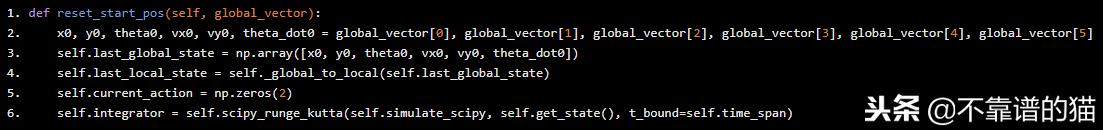
我们还必须定义step函数。代理在导航时使用此函数,在每个step中,代理选择一个动作并在10秒内(在我们的积分器中)运行模拟并一次又一次地执行,直到它到达通道末端或直到它到达通道边缘。
def step(self, action): side = np.sign(self.last_pos[1]) angle_action = action[0]*side rot_action = 0.2 state_prime = self.simulator.step(angle_level=angle_action, rot_level=rot_action) # convert simulator states into obervable states obs = self.convert_state(state_prime) # print('Observed state: ', obs) dn = self.end(state_prime=state_prime, obs=obs) rew = self.calculate_reward(obs=obs) self.last_pos = [state_prime[0], state_prime[1], state_prime[2]] self.last_action = np.array([angle_action, rot_action]) info = dict() return obs, rew, dn, info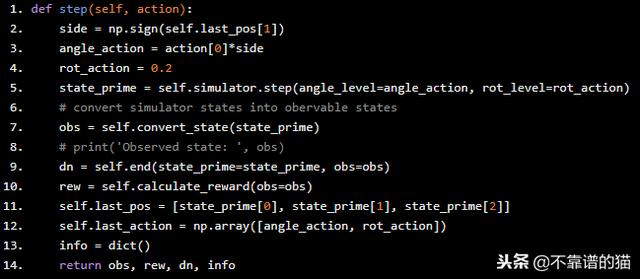
最后,我们定义了设置init space-state和reset函数,它们在每次新迭代的开始使用。
def set_init_space(self, low, high): self.init_space = spaces.Box(low=np.array(low), high=np.array(high))def reset(self): init = list(map(float, self.init_space.sample())) init_states = np.array([self.start_pos[0], init[0], init[1], init[2] * np.cos(init[1]), init[2] * np.sin(init[1]), 0]) self.simulator.reset_start_pos(init_states) self.last_pos = np.array([self.start_pos[0], init[0], init[1]]) print('Reseting position') state = self.simulator.get_state() if self.viewer is not None: self.viewer.end_episode() return self.convert_state(state)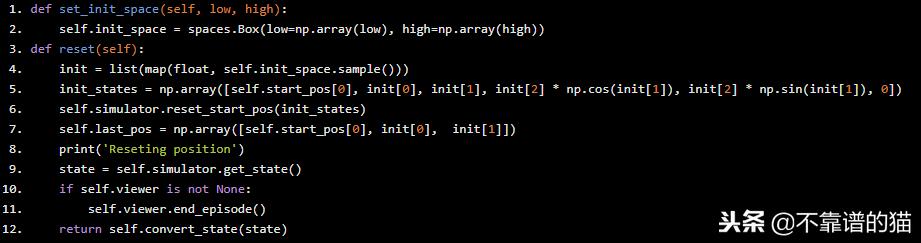
最后,经过训练,我们得到以下结果:代理已经学会了如何控制方向舵以及如何在中途保持通道。
更详细的船模型,还包括由AI代理控制的推进动作。可以在此处找到项目存储库。
相关文章









猜你喜欢